Embarking on an exploration of pogil cell cycle regulation answers, we delve into a realm of intricate cellular processes that govern the very foundation of life. This journey unveils the fundamental principles that orchestrate cell division, ensuring the precise replication and transmission of genetic material.
From the meticulous phases of the cell cycle to the pivotal checkpoints that safeguard its integrity, we unravel the molecular mechanisms that underpin this remarkable biological phenomenon.
Unraveling the intricacies of cell cycle regulation, we uncover the pivotal role of cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) as conductors of cell cycle progression. We delve into the intricate interplay of phosphorylation and ubiquitination in modulating CDK activity, illuminating the precise mechanisms that govern the timely progression through the cell cycle.
Cell Cycle Regulation Overview: Pogil Cell Cycle Regulation Answers
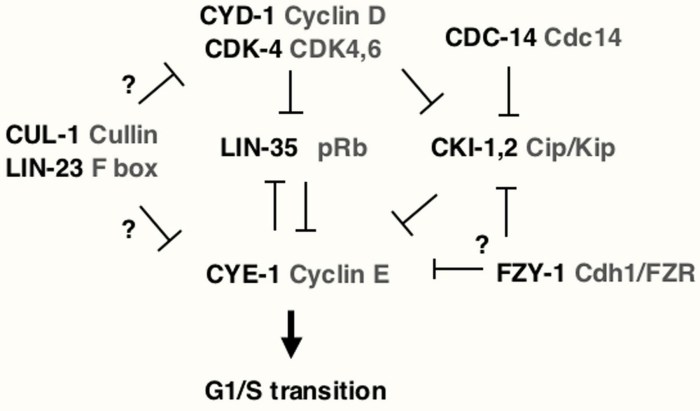
The cell cycle is a tightly regulated process that ensures the accurate duplication and division of cells. It consists of four distinct phases: G1, S, G2, and M. During the G1 phase, the cell grows and prepares for DNA replication.
In the S phase, DNA replication occurs. The G2 phase provides time for the cell to check for DNA damage and repair any errors. Finally, in the M phase, the cell divides into two daughter cells.The cell cycle is regulated by a complex network of checkpoints that ensure that each phase is completed successfully before the cell proceeds to the next phase.
The most important checkpoints are the G1/S checkpoint, the G2/M checkpoint, and the M checkpoint.
Mechanisms of Cell Cycle Regulation
The cell cycle is regulated by a family of proteins called cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs). Cyclins bind to CDKs and activate them. The activated CDKs then phosphorylate other proteins, which triggers the events of the cell cycle.The activity of CDKs is tightly regulated by phosphorylation and ubiquitination.
Phosphorylation can activate or inhibit CDKs, while ubiquitination targets them for degradation.
External Factors Influencing Cell Cycle Regulation
The cell cycle is also influenced by external factors, such as growth factors, hormones, and environmental cues. Growth factors are proteins that stimulate cell growth and division. Hormones are chemical messengers that regulate a variety of cellular processes, including the cell cycle.
Environmental cues, such as temperature and radiation, can also affect the cell cycle.These external factors transmit signals to the cell cycle machinery through a variety of mechanisms. For example, growth factors bind to receptors on the cell surface, which triggers a cascade of events that leads to the activation of CDKs.
Dysregulation of Cell Cycle Regulation
Dysregulation of cell cycle regulation can lead to a variety of problems, including uncontrolled cell proliferation and tumor formation. Uncontrolled cell proliferation can occur when the cell cycle checkpoints are not functioning properly. This can lead to the accumulation of mutations in the cell’s DNA, which can eventually lead to cancer.The
molecular mechanisms underlying cell cycle deregulation in cancer cells are complex and vary depending on the type of cancer. However, some common mechanisms include the overexpression of cyclins, the mutation of CDKs, and the inactivation of cell cycle checkpoints.
Experimental Techniques for Studying Cell Cycle Regulation, Pogil cell cycle regulation answers
There are a variety of experimental techniques that can be used to study cell cycle regulation. These techniques include flow cytometry, immunofluorescence microscopy, and genetic and biochemical techniques.Flow cytometry is a technique that can be used to measure the cell cycle distribution of a population of cells.
Immunofluorescence microscopy is a technique that can be used to visualize the expression of cell cycle proteins in individual cells. Genetic and biochemical techniques can be used to investigate the molecular mechanisms of cell cycle regulation.
Questions Often Asked
What are the key checkpoints in the cell cycle and their significance?
The key checkpoints in the cell cycle are the G1/S checkpoint, the G2/M checkpoint, and the M checkpoint. These checkpoints ensure that the cell has completed the necessary preparations for the next phase of the cell cycle and that the DNA is not damaged.
How do cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) regulate cell cycle progression?
Cyclins and CDKs form complexes that phosphorylate target proteins, which in turn regulate the progression of the cell cycle. For example, the cyclin-CDK complex phosphorylates proteins that are involved in DNA replication, which is necessary for the cell to enter the S phase.
How can external factors influence cell cycle regulation?
External factors such as growth factors, hormones, and environmental cues can influence cell cycle regulation by activating or inhibiting specific signaling pathways. For example, growth factors can activate the PI3K/Akt pathway, which leads to the activation of cyclin D and the progression of the cell cycle.