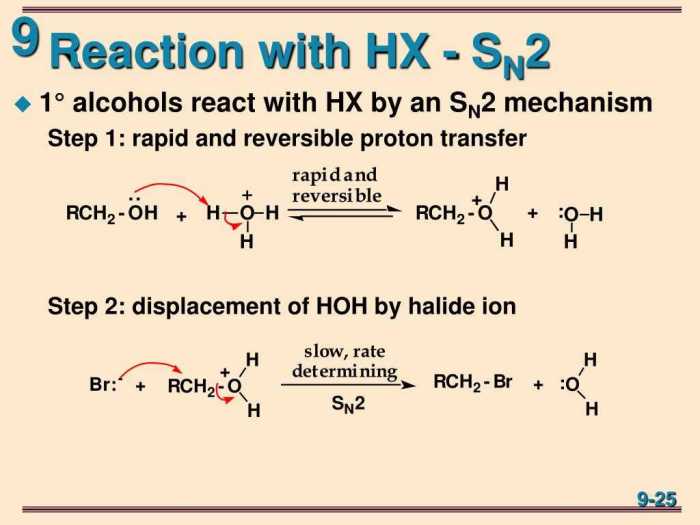
Introducing topic 9 oxidation reduction answer key, this comprehensive guide delves into the fascinating world of chemical reactions, shedding light on the fundamental concepts of oxidation and reduction. By exploring real-world examples, we unravel the intricate mechanisms behind these reactions, empowering you with a deeper understanding of their significance.
As we navigate through this topic, we will uncover the role of oxidizing and reducing agents, delve into the art of balancing redox reactions, and categorize various types of redox reactions. Additionally, we will explore the diverse applications of redox reactions, spanning from electrochemistry to biological processes, showcasing their profound impact on our world.
Oxidation-Reduction Reactions: Topic 9 Oxidation Reduction Answer Key
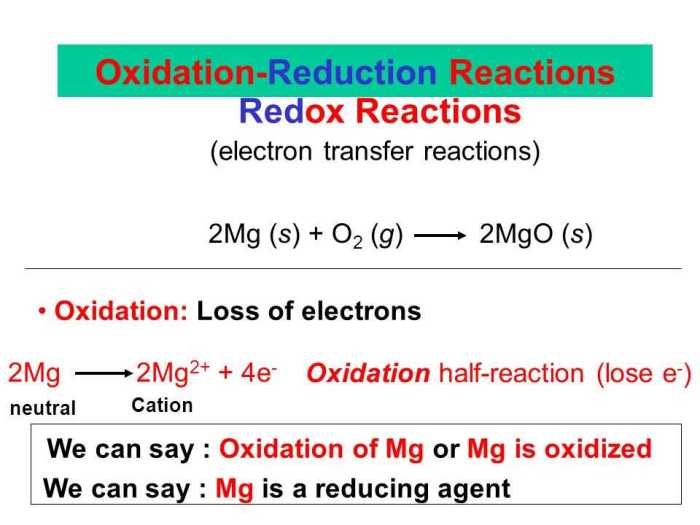
Oxidation-reduction (redox) reactions involve the transfer of electrons between atoms or ions. Oxidation is the loss of electrons, while reduction is the gain of electrons. Redox reactions play a crucial role in various chemical processes and have numerous applications in science and technology.
Role of Oxidizing and Reducing Agents
In a redox reaction, the substance that causes oxidation is called the oxidizing agent, and the substance that causes reduction is called the reducing agent. The oxidizing agent undergoes reduction, and the reducing agent undergoes oxidation.
Balancing Redox Reactions
Balancing redox reactions requires the use of the half-reaction method, which involves separating the reaction into two half-reactions: one for oxidation and one for reduction. The half-reactions are then balanced for mass and charge before combining them to form the overall balanced redox reaction.
Use of Oxidation Numbers
Oxidation numbers are used to keep track of the electron transfer in redox reactions. An oxidation number represents the hypothetical charge an atom would have if all its bonds were ionic. Oxidation numbers are used to determine the change in oxidation state of atoms during a redox reaction, which helps in balancing the half-reactions.
Types of Redox Reactions, Topic 9 oxidation reduction answer key
- Combination reactions:Two or more substances combine to form a single product.
- Decomposition reactions:A single substance breaks down into two or more products.
- Displacement reactions:A more reactive element displaces a less reactive element from a compound.
- Disproportionation reactions:A single substance undergoes both oxidation and reduction to form two different products.
Applications of Redox Reactions
Redox reactions have numerous applications, including:
- Electrochemistry:Redox reactions are the basis of electrochemical cells, such as batteries and fuel cells.
- Corrosion:Redox reactions are responsible for the corrosion of metals, which can be prevented using protective coatings or cathodic protection.
- Batteries:Redox reactions occur in batteries, where chemical energy is converted into electrical energy.
- Biological processes:Redox reactions are involved in many biological processes, such as respiration and photosynthesis.
Commonly Asked Questions
What is the difference between oxidation and reduction?
Oxidation refers to the loss of electrons, while reduction refers to the gain of electrons.
How do you balance redox reactions?
Redox reactions can be balanced using the half-reaction method or the oxidation number method.
What are the different types of redox reactions?
There are four main types of redox reactions: combination reactions, decomposition reactions, displacement reactions, and disproportionation reactions.