The Imperialism and America Worksheet Answers delves into the intricate history, motivations, and consequences of American imperialism, offering a comprehensive understanding of this complex phenomenon. This meticulously crafted guide provides a comprehensive exploration of the topic, empowering learners with a profound grasp of the subject matter.
Throughout history, American imperialism has manifested in various forms, driven by a multitude of factors. This worksheet unravels the methods employed by the United States to exert its imperial control, including political, economic, and military strategies. Furthermore, it examines the profound impact of American imperialism on indigenous populations and foreign territories.
Imperialism and America: Historical Context

Imperialism refers to the extension of political and economic control by a powerful nation over weaker territories or peoples. The origins of imperialism can be traced back to the era of European colonialism, when European powers established empires across the globe.
American imperialism emerged as the United States expanded its influence beyond its borders in the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
American imperialism has been motivated by a complex set of factors, including economic interests, strategic concerns, and a sense of national destiny. The United States has pursued imperial policies through various means, such as military intervention, economic coercion, and diplomatic pressure.
Methods and Manifestations of American Imperialism
The United States has employed a range of methods to exert imperial control, including:
- Military intervention:The US has used military force to acquire and maintain control over territories, such as the Spanish-American War (1898) and the invasion of Iraq (2003).
- Economic coercion:The US has used its economic power to pressure other countries into accepting its demands, such as the use of sanctions against Cuba.
- Diplomatic pressure:The US has used its diplomatic influence to shape the policies of other countries, such as the Monroe Doctrine (1823), which declared the Western Hemisphere to be under US protection.
American imperialism has had a profound impact on the indigenous populations and foreign territories it has controlled. The US has often imposed its own political and economic systems on these territories, leading to cultural and economic disruption.
Imperialism and the American Identity
Imperialism has played a significant role in shaping American national identity. The expansion of the US empire has been seen as a source of national pride and a symbol of American power. However, imperialism has also been a source of controversy and debate within the United States.
Critics of American imperialism argue that it has been a source of oppression and exploitation. They point to the negative consequences of US imperialism, such as the displacement of indigenous populations, the destruction of local economies, and the spread of American cultural hegemony.
Consequences and Legacies of American Imperialism, Imperialism and america worksheet answers
The consequences of American imperialism have been far-reaching. The US has emerged as a global superpower, but its imperial policies have also had negative consequences for the United States and the world.
Positive consequences:
- Economic growth: Imperialism has contributed to the economic growth of the United States by providing access to new markets and resources.
- National security: Imperialism has allowed the US to secure its strategic interests and protect its borders.
Negative consequences:
- Human rights violations: The US has been accused of human rights violations in the territories it has controlled, such as the use of torture and the suppression of dissent.
- Economic inequality: Imperialism has contributed to economic inequality within the United States, as the benefits of imperialism have been unevenly distributed.
Case Studies of American Imperialism
There are numerous case studies of American imperialism, including:
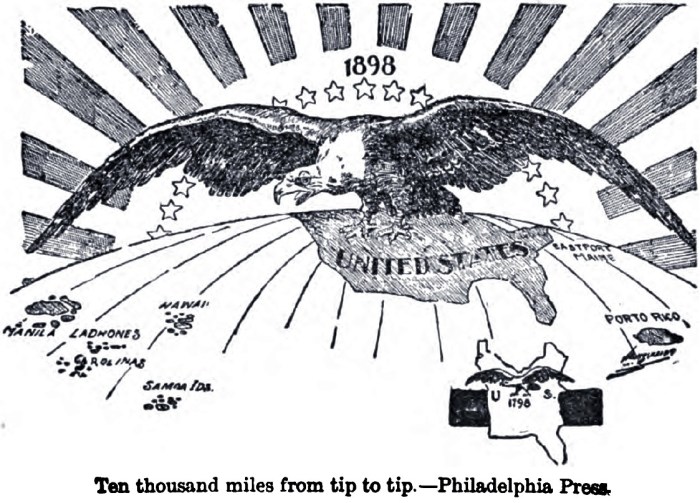
- The Philippines:The US acquired the Philippines from Spain in 1898. The US ruled the Philippines for nearly 50 years, during which time it suppressed local rebellions and exploited the country’s natural resources.
- Cuba:The US intervened in Cuba’s war for independence from Spain in 1898. The US established a protectorate over Cuba and maintained significant influence over the country’s affairs until the Cuban Revolution in 1959.
- Hawaii:The US annexed Hawaii in 1898. The US sugar industry played a major role in the annexation of Hawaii, and the US has maintained a strong military presence in Hawaii since then.
FAQ Overview: Imperialism And America Worksheet Answers
What are the key characteristics of imperialism?
Imperialism involves the extension of political and economic control by one country over another, often through military force or economic coercion.
How did American imperialism manifest in the Philippines?
American imperialism in the Philippines involved the establishment of a colonial government, the suppression of local resistance, and the exploitation of natural resources.
What were the motivations behind American imperialism in Cuba?
American imperialism in Cuba was driven by economic interests, particularly the desire to control the sugar industry, and by strategic concerns related to the Spanish-American War.